subpixel averaging for boundaries of variable-material objects #1399
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
This PR implements subpixel averaging for the boundaries of objects with variable materials (e.g. user-defined material functions). I realized that we can still handle this case accurately and efficiently, as long as the material function is continuous inside the object.
For example, here is a simulation of transmitted power through a cylinder of linearly-varying ε:

If I compute and plot the convergence with respect to resolution using this code:
then before this PR I get first-order convergence due to the lack of subpixel averaging at the boundaries of the cylinder:
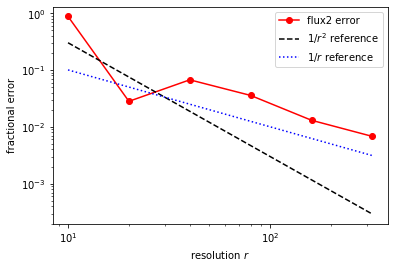
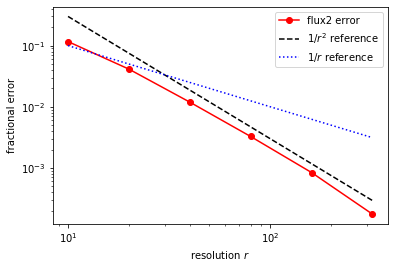
but after this PR I get second-order convergence: